
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) was designed to respond to these needs. Additionally, the development for the World Wide Web, while making some things simpler, has exacerbated these architectural problems. In particular, they recognize the need to solve recurring architectural problems, such as physical distribution, concurrency, replication, security, load balancing and fault tolerance. Businesses also seek techniques to manage the complexity of systems as they increase in scope and scale. These techniques include component technology, visual programming, patterns and frameworks.
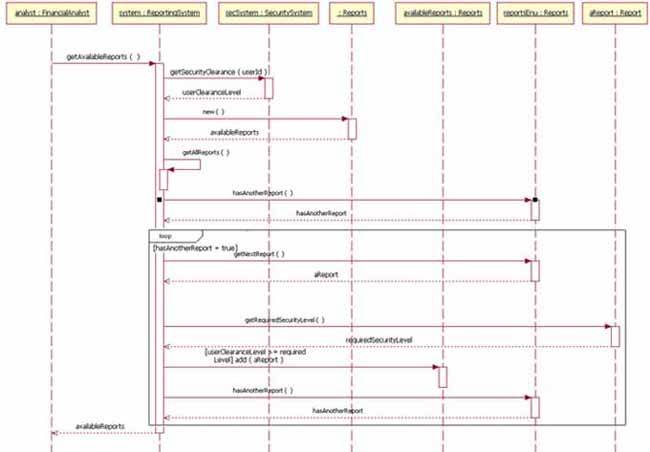
#Sequence diagram example simple software
It was submitted to the OMG for their consideration and adopted in the fall of 1997.1 and enhanced 1.1 to 1.5, and subsequently to UML 2.1 from 01 to 06 (now the UML current version is 2.5)Īs the strategic value of software increases for many companies, the industry looks for techniques to automate the production of software and to improve quality and reduce cost and time-to-market. The focus of the UML 1.1 release was to improve the clarity of the UML 1.0 semantics and to incorporate contributions from the new partners. These companies joined the UML partners to contribute their ideas, and together the partners produced the revised UML 1.1 response.
During 1996, the first Request for Proposal (RFP) issued by the Object Management Group (OMG) provided the catalyst for these organizations to join forces around producing a joint RFP response.UML also includes new concepts that were not present in other major methods at the time, such as extension mechanisms and a constraint language. UML has also been influenced by other object-oriented notations: The team of Rumbaugh, Booch and Jacobson are affectionately known as the "Three Amigos" The aim of the partnership was to merge their ideas into a single, unified method (the working title for the method was indeed the "Unified Method").īy 1995, the creator of OOSE, Ivar Jacobson, had also joined Rational, and his ideas (particularly the concept of "Use Cases") were fed into the new Unified Method - now called the Unified Modelling Language1. In 1994, Jim Rumbaugh, the creator of OMT, stunned the software world when he left General Electric and joined Grady Booch at Rational Corp. Use Cases are a powerful technique for understanding the behaviour of an entire system (an area where OO has traditionally been weak).

OOSE (Object-Oriented Software Engineering ) - featured a model known as Use Cases.Although the Booch method was strong, the notation was less well received (lots of cloud shapes dominated his models - not very tidy) Grady Booch had worked extensively with the Ada language, and had been a major player in the development of Object Oriented techniques for the language.




 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
